Probiotics for Gut Health: Effective Strains for Digestive Issues

Probiotics play a crucial role in gut health by introducing beneficial bacteria that can alleviate digestive issues, with strains like *Lactobacillus* and *Bifidobacterium* showing significant effectiveness in managing conditions such as IBS and bloating.
Embarking on a journey to improve your digestive health? The answer might lie in the tiny world of probiotics. Let’s explore the role of probiotics in gut health: which strains are most effective for digestive issues?
Understanding the Gut Microbiome and Its Importance
The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract, plays a pivotal role in overall health. Its balance, or lack thereof, can significantly impact digestion, immunity, and even mental well-being.
The gut microbiome is not just a collection of bacteria; it’s an ecosystem. Understanding this ecosystem is the first step in appreciating the potential of probiotics.
What is the Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome is composed of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms. These microbes aid in digesting food, synthesizing vitamins, and protecting against harmful pathogens. A healthy gut microbiome is diverse, with a wide range of species working in harmony.
An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various health issues, including digestive disorders, inflammation, and weakened immunity.
Factors Affecting Gut Microbiome Health
Several factors can influence the composition and health of the gut microbiome, including diet, antibiotics, stress, and lifestyle. A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, while a diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables promotes diversity and overall health.
- Diet: A diet rich in fiber and diverse plant-based foods nourishes beneficial gut bacteria.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics can kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria, disrupting the gut microbiome.
- Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiome, leading to dysbiosis.
- Lifestyle: Factors like sleep, exercise, and exposure to environmental toxins can also play a role.
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome requires a holistic approach that considers all these factors.
In summary, the gut microbiome is a dynamic ecosystem that requires careful nurturing. Understanding its importance and the factors that influence its health is key to promoting digestive wellness and overall well-being.
What are Probiotics and How Do They Work?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. They work by introducing beneficial bacteria into the gut, helping to restore balance and improve digestive function.
Probiotics are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different strains have different effects, and understanding these differences is crucial to choosing the right probiotic for your needs.
How Probiotics Work
Probiotics exert their beneficial effects through several mechanisms. They can help to crowd out harmful bacteria, strengthen the gut barrier, and modulate the immune system. By competing with pathogens for resources and attachment sites, probiotics can prevent them from colonizing the gut and causing infection.
Furthermore, probiotics can produce substances that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, such as lactic acid and bacteriocins.
Sources of Probiotics
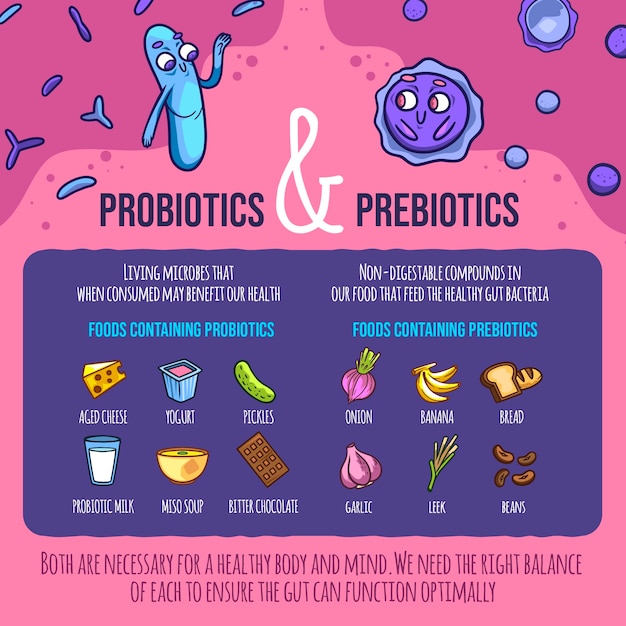
Probiotics can be obtained from various sources, including fermented foods, dietary supplements, and pharmaceutical products. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are natural sources of probiotics. However, the specific strains and amounts of probiotics in these foods can vary widely.
Dietary supplements offer a more controlled way to consume probiotics, as they typically contain specific strains and amounts of bacteria. Pharmaceutical products containing probiotics are also available for certain medical conditions.
Choosing the right source of probiotics depends on individual preferences and needs.
In conclusion, probiotics are a valuable tool for promoting gut health by introducing beneficial bacteria and restoring balance to the gut microbiome. Understanding how probiotics work and where to find them is essential for making informed choices about their use.
Effective Probiotic Strains for Common Digestive Issues
Certain probiotic strains have demonstrated particular effectiveness in addressing specific digestive issues. Knowing which strains target which symptoms can help individuals make informed choices about probiotic supplementation.
Not all probiotic strains are created equal. Some strains are more effective for certain conditions than others.
Lactobacillus Strains
Lactobacillus strains are among the most well-studied and widely used probiotics. They are particularly effective in managing diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain. *Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG* is one example that has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and traveler’s diarrhea.
*Lactobacillus reuteri* is another strain that has been found to improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), such as abdominal pain and bloating.
Bifidobacterium Strains
Bifidobacterium strains are commonly found in the gut and play a key role in maintaining gut health. They are particularly effective in managing constipation and improving bowel regularity. *Bifidobacterium lactis* is a well-studied strain that has been shown to improve stool consistency and frequency in individuals with constipation.
*Bifidobacterium infantis* is another strain that has been found to reduce symptoms of IBS, such as bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Other Beneficial Strains
In addition to Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, other probiotics have also shown promise in managing digestive issues. *Saccharomyces boulardii* is a yeast probiotic that has been found to be effective in preventing and treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: Reduces duration and severity of diarrhea.
- Bifidobacterium lactis: Improves stool consistency and frequency in constipation.
- Saccharomyces boulardii: Prevents and treats antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
These diverse strains offer a range of benefits for various digestive conditions.
In brief, selecting the right probiotic strain is crucial for addressing specific digestive issues. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains are among the most well-studied and widely used, but other probiotics like Saccharomyces boulardii can also offer significant benefits.
Probiotics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and altered bowel habits. Probiotics have emerged as a promising complementary therapy for managing IBS symptoms.
IBS is a complex condition with various subtypes and triggers. Probiotics can help alleviate symptoms by addressing gut dysbiosis and inflammation.
How Probiotics Help with IBS
Probiotics can help to alleviate IBS symptoms by restoring balance to the gut microbiome, reducing inflammation, and improving gut barrier function. Certain strains have been specifically studied for their effectiveness in managing IBS symptoms.
For example, *Bifidobacterium infantis 35624* has been shown to reduce abdominal pain, bloating, and gas in individuals with IBS. *Lactobacillus plantarum 299v* has also been found to improve symptoms of IBS and enhance quality of life.
Choosing the Right Probiotic for IBS
When selecting a probiotic for IBS, it’s important to choose a strain that has been specifically studied for its effectiveness in managing IBS symptoms. Combination products containing multiple strains may also be beneficial.
It’s also important to consider the individual’s specific IBS symptoms. For example, individuals with constipation-predominant IBS may benefit from probiotics that promote bowel regularity, while those with diarrhea-predominant IBS may benefit from probiotics that reduce diarrhea.
Consulting with a healthcare professional can help individuals choose the right probiotic for their specific IBS symptoms.
Overall, probiotics offer a valuable tool for managing IBS symptoms by restoring balance to the gut microbiome and reducing inflammation. Selecting the right probiotic strain based on individual symptoms and consulting with a healthcare professional can maximize the benefits.
The Role of Probiotics in Preventing and Treating Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a common digestive issue that can be caused by various factors, including infections, antibiotics, and dietary changes. Probiotics have been shown to be effective in preventing and treating different types of diarrhea.
Probiotics can help to restore balance to the gut microbiome, reduce inflammation, and boost the immune system.
Probiotics for Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) is a common side effect of antibiotic use, as antibiotics can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome. Probiotics can help to prevent and treat AAD by replenishing beneficial bacteria in the gut.
*Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG* and *Saccharomyces boulardii* are two of the most well-studied probiotics for AAD. These strains have been shown to reduce the risk and severity of AAD when taken alongside antibiotics.
Probiotics for Traveler’s Diarrhea
Traveler’s diarrhea is another common type of diarrhea that occurs when traveling to areas with poor sanitation. Probiotics can help to prevent traveler’s diarrhea by strengthening the gut barrier and boosting the immune system.
- Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea: *Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG* and *Saccharomyces boulardii* are effective.
- Traveler’s Diarrhea: Probiotics strengthen the gut barrier and boost immunity.
- Infectious Diarrhea: Probiotics can shorten the duration of illness.
*Saccharomyces boulardii* has been shown to be particularly effective in preventing traveler’s diarrhea when taken before and during travel.
In conclusion, probiotics offer a valuable tool for preventing and treating various types of diarrhea by restoring balance to the gut microbiome and boosting the immune system. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Saccharomyces boulardii are two of the most well-studied and widely used probiotics for diarrhea.
How to Choose the Right Probiotic Supplement
With so many probiotic supplements on the market, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. Understanding the key factors to consider can help individuals make informed choices.
Not all probiotic supplements are created equal. Factors like strain specificity, CFU count, and product quality can significantly impact their effectiveness.
Consider the Specific Strains
As mentioned earlier, different probiotic strains have different effects. Therefore, it’s important to choose a probiotic supplement that contains strains that have been specifically studied for the digestive issue you’re trying to address. Look for products that list the specific strains (e.g., *Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG*) on the label.
Avoid products that only list the genus and species (e.g., *Lactobacillus*) without specifying the strain.
Check the CFU Count
CFU stands for colony-forming units, which is a measure of the number of live bacteria in a probiotic supplement. Look for products that contain at least 1 billion CFU per dose. Higher CFU counts may be beneficial for certain conditions, but it’s generally not necessary to exceed 10 billion CFU per dose.
Also, check the expiration date to ensure that the product contains the stated number of CFU at the time of consumption.
Look for Quality Certifications
Choose probiotic supplements from reputable manufacturers that have undergone third-party testing for quality and purity. Look for certifications from organizations like USP, NSF International, or ConsumerLab.com. These certifications indicate that the product has been tested for potency, purity, and contaminants.
Store probiotic supplements according to the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain their potency.
In short, selecting the right probiotic supplement involves considering strain specificity, CFU count, and product quality. Choosing products from reputable manufacturers and consulting with a healthcare professional can help individuals make informed choices about probiotic supplementation.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌱 Gut Microbiome | Complex ecosystem affecting digestion, immunity, and mental health. |
| 💪 Probiotics | Live microorganisms improving gut balance and digestive function. |
| 🦠 IBS Relief | Specific strains reduce abdominal pain, bloating, and gas. |
| 🛡️ Diarrhea Prevention | Certain strains prevent and treat antibiotic-associated diarrhea. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
Probiotics can improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, boost the immune system, and reduce the risk of digestive disorders such as IBS and diarrhea by restoring balance in the gut.
▼
The time it takes for probiotics to show effects varies, but many people notice improvements in digestion, bloating, or bowel regularity within a few days to a few weeks of consistent use.
▼
Probiotics are generally safe, but some people may experience mild side effects like gas, bloating, or changes in bowel habits, especially when starting a new supplement. These effects usually subside quickly.
▼
While fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain probiotics, the amounts and strains can vary. A probiotic supplement can provide a more consistent and targeted dose of specific strains.
▼
Some studies suggest taking probiotics with food can improve their survival rate in the digestive system. However, it’s best to follow the specific recommendations on the supplement label for optimal absorption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the role of probiotics in maintaining and restoring gut health is increasingly important. By choosing the right strains for specific digestive issues and following best practices for supplementation, individuals can harness the full potential of probiotics to improve their overall well-being.
