How to Read Nutrition Labels in 2025: A Guide to Added Sugars & Sodium
How to Read Nutrition Labels in 2025: A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Added Sugars and Sodium Content provides consumers with the knowledge to navigate nutrition labels effectively, focusing on critical aspects like added sugars and sodium content for informed dietary choices.
Navigating the grocery store aisles can feel like deciphering a secret code, especially when it comes to nutrition labels. But fear not! This comprehensive guide, How to Read Nutrition Labels in 2025: A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Added Sugars and Sodium Content, is here to equip you with the knowledge you need to make healthier choices.
Understanding the Basics of Nutrition Labels
Nutrition labels are designed to provide consumers with essential information about the nutritional content of packaged foods and beverages. Learning how to interpret these labels is a crucial step towards making informed decisions about your diet and overall health. This section covers the vital components found on every label.
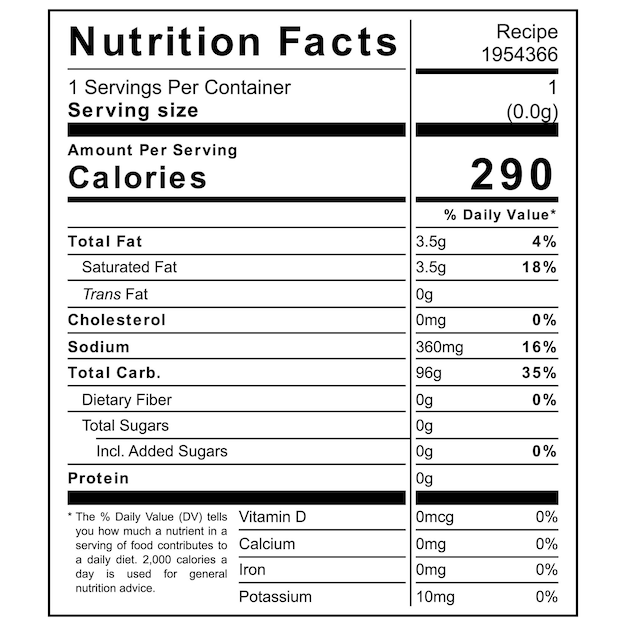
What’s on a Nutrition Label?
The nutrition label, officially called the “Nutrition Facts” label, is a standardized format required on most packaged foods. It includes information about serving size, calories, macronutrients (fat, carbohydrates, protein), vitamins, and minerals. Let’s explore some key elements:
- Serving Size: This indicates the amount of food typically consumed in one serving. All the nutrient amounts listed on the label are based on this serving size.
- Calories: This shows the total number of calories in one serving.
- Macronutrients: This section breaks down the amount of fat, carbohydrates, and protein in grams per serving.
- Vitamins and Minerals: This lists the percentage of the Daily Value (DV) for certain vitamins and minerals in one serving.
Understanding these basics is the foundation for making healthier choices. But, in 2025, there are some specific areas you’ll want to pay extra attention to.
Why Are Nutrition Labels Important?
Nutrition labels play a vital role in helping individuals monitor their nutrient intake and make informed food choices. They empower consumers to:
- Compare Products: Easily compare the nutritional content of different brands or similar products.
- Manage Health Conditions: Individuals with diabetes, heart disease, or other health conditions can use labels to control their intake of specific nutrients.
- Meet Dietary Goals: People trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply eat healthier can use labels to track their progress and ensure they meet their nutritional needs.
- Avoid Allergens: Although not always part of the Nutrition Facts panel, labels often include allergen warnings.
Regularly using nutrition labels can lead to improved dietary habits and better health outcomes. Knowing what’s in your food is the first step to taking control of your well-being. By understanding these fundamental components, you’re better prepared to dive into the specifics of added sugars and sodium.
In conclusion, grasping the basics of nutrition labels empowers you to make informed choices and take control of your dietary habits. Becoming proficient in interpreting these labels sets the stage for a healthier lifestyle.
Decoding Added Sugars: What to Look For
One of the most significant changes to nutrition labels in recent years is the inclusion of “Added Sugars.” This addition helps consumers differentiate between naturally occurring sugars (like those in fruit) and sugars that are added during processing. Knowing how to decode this information is essential for maintaining a healthy diet.
Identifying Added Sugars on the Label
The “Added Sugars” line on the nutrition label indicates the amount of sugars that have been added to the product during processing. This includes sugars like table sugar (sucrose), high-fructose corn syrup, and honey. It’s important to note that the “Total Sugars” line includes both naturally occurring and added sugars. Here are some key points to consider:
- Look for “Added Sugars”: This line is typically located directly below the “Total Sugars” line.
- Check the Grams: The number of grams indicates the amount of added sugars per serving.
- Consider the % Daily Value (DV): This percentage tells you how much the added sugars in one serving contribute to the recommended daily limit.
Aim to minimize your intake of added sugars to reduce your risk of health problems like weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Why Are Added Sugars a Concern?
Unlike naturally occurring sugars, added sugars provide little to no nutritional value. Consuming too much added sugar can lead to a variety of health issues, including:
- Weight Gain: Added sugars are high in calories and can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
- Type 2 Diabetes: High sugar intake can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by impairing insulin function.
- Heart Disease: Studies have shown a link between high added sugar consumption and an increased risk of heart disease.
- Tooth Decay: Sugars feed bacteria in your mouth, leading to tooth decay and cavities.

By paying attention to the “Added Sugars” information on nutrition labels, you can make more informed choices and reduce your intake of these potentially harmful ingredients.
In summary, understanding the “Added Sugars” line on nutrition labels is crucial for making health-conscious choices. By minimizing your intake of added sugars, you can reduce your risk of various health problems and improve your overall well-being.
Sodium Content: Finding and Interpreting the Data
Sodium, a key component of salt, is an essential nutrient, but most Americans consume far more than the recommended amount. High sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Learning how to identify and interpret sodium content on nutrition labels is vital for maintaining a healthy heart.
Locating Sodium Information on the Label
The sodium content is clearly listed on the nutrition label in milligrams (mg) per serving. It’s typically found in the “Macronutrients” section, along with fat, carbohydrates, and protein. Here’s what to look for:
- Sodium (mg): This indicates the amount of sodium in milligrams per serving.
- % Daily Value (DV): This percentage tells you how much the sodium in one serving contributes to the recommended daily limit. The DV for sodium is less than 2,300 mg per day.
Pay close attention to both the milligrams of sodium and the % Daily Value to make informed choices about your sodium intake.
Why Monitoring Sodium Matters
Excessive sodium intake can have serious health consequences, including:
- High Blood Pressure: Sodium increases blood volume, which can lead to high blood pressure.
- Heart Disease and Stroke: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Kidney Problems: Excessive sodium can strain the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease.
By monitoring your sodium intake and choosing lower-sodium options, you can reduce your risk of these health problems.
To summarize, sodium is important for the body, but harmful in excess. Being able to locate sodium information on nutrition labels and interpreting Sodium content correctly, you’ll be much more equipped to manage your health and keep heart and kidney problems at bay.
Tips for Reducing Sodium Intake
Reducing sodium intake doesn’t have to be difficult. Here are some simple tips to help you lower your sodium consumption:
- Read Labels Carefully: Always check the nutrition label for sodium content before buying a product.
- Choose Low-Sodium Options: Look for products labeled “low sodium,” “reduced sodium,” or “no salt added.”
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the amount of sodium you add to your food.
- Use Herbs and Spices: Flavor your food with herbs, spices, and citrus juices instead of salt.
By following these tips, you can effectively reduce your sodium intake and improve your overall health.
Serving Size vs. Actual Consumption
One of the most common pitfalls when reading nutrition labels is overlooking the serving size. The information on the label is based on a specific serving size, which may not always align with the amount you actually consume. Understanding this discrepancy is crucial for accurately assessing your nutrient intake.
The Importance of Serving Size Awareness
The serving size is a standardized amount of food that is used to calculate the nutrient information on the label. It’s essential to pay attention to the serving size because consuming more or less than the listed amount will directly impact your intake of calories, sugars, sodium, and other nutrients. For instance:
- Double the Serving: If you eat two servings, you’re consuming twice the calories, sugars, and sodium listed on the label.
- Half the Serving: If you eat half a serving, you’re consuming half the calories, sugars, and sodium listed on the label.
Always compare the serving size on the label to the amount you actually eat to get an accurate picture of your nutrient intake.
Practical Tips for Accurate Measurement
To ensure you’re accurately measuring your portions, consider these practical tips:
- Use Measuring Cups and Spoons: Use standard measuring cups and spoons to portion out your food.
- Weigh Your Food: A food scale can provide even more accurate measurements, especially for items like meat and cheese.
- Read the Label Carefully: Pay close attention to the serving size and units (e.g., cups, ounces, grams) listed on the label.
- Portion Out Snacks: Instead of eating directly from the package, portion out snacks into individual servings.
By taking these steps, you can avoid overeating and accurately track your nutrient intake.

Real-Life Examples
To illustrate the importance of serving size, consider these real-life examples:
Many people consume more than one serving of these items without realizing it, leading to a significant increase in their calorie, sugar, and sodium intake. Paying attention to serving sizes can help you make more informed choices and avoid overconsumption.
In conclusion, remember that information on nutrition labels are calculated around serving sizes, and the amount you’re supposed to consume versus what you actually consume can differ greatly. To maintain control of your health, follow the practical tips to help measure and avoid overeating.
The Future of Nutrition Labels: What to Expect in 2025
As our understanding of nutrition evolves, so do the regulations and formats of nutrition labels. By 2025, we can anticipate further changes and enhancements designed to provide consumers with even more clarity and actionable information.
Anticipated Changes in Labeling Regulations
While specific regulatory changes can vary by country and region, some common trends are expected to influence the future of nutrition labels:
- Front-of-Package Labeling (FOPL): More widespread adoption of FOPL systems, which use symbols or ratings to quickly convey the overall nutritional quality of a food product.
- Enhanced Ingredient Information: Clearer and more detailed listing of ingredients, including highlighting potential allergens and additives.
- Emphasis on Sustainability: Inclusion of information related to the environmental impact of food production and packaging.
- Digital Integration: Increased use of QR codes or other digital technologies to provide access to more detailed nutritional information and personalized dietary recommendations.
These changes aim to make nutrition labels more user-friendly and relevant to consumers’ evolving needs.
The Role of Technology in Nutrition Monitoring
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in helping individuals track their nutrient intake and make healthier choices. In 2025, we can expect to see even more sophisticated tools and apps that integrate with nutrition labels:
- Label Scanning Apps: Apps that allow you to scan nutrition labels and instantly access detailed information about the product, including potential health risks and benefits.
- Personalized Nutrition Recommendations: Apps that provide customized dietary recommendations based on your individual needs, preferences, and health goals.
- Wearable Devices: Devices that track your physical activity and calorie expenditure, helping you balance your energy intake and maintain a healthy weight.
By leveraging these technologies, you can gain a deeper understanding of your dietary habits and make more informed choices.
Preparing for the Future of Food Labeling
To stay ahead of the curve and make the most of future nutrition labels, consider these tips:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest news and regulations related to food labeling.
- Embrace Technology: Explore and experiment with different apps and tools that can help you track your nutrient intake and make healthier choices.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Continue to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods and limit your intake of added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats.
By preparing for the future of food labeling, you can take control of your health and make informed choices that support your well-being.
Making Informed Choices: Putting It All Together
Reading nutrition labels is more than just understanding the individual components; it’s about putting all the information together to make informed choices that align with your health goals. By integrating your understanding of serving sizes, added sugars, sodium content, and other key nutrients, you can create a balanced and nutritious diet.
Developing a Holistic Approach to Nutrition
A holistic approach to nutrition involves considering the overall nutritional quality of your diet, rather than focusing on individual nutrients in isolation. This means:
- Prioritizing Whole Foods: Focus on filling your diet with whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limiting Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of processed foods, which are often high in added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats.
- Balancing Macronutrients: Ensure you’re getting an adequate balance of macronutrients (fat, carbohydrates, protein) to support your energy needs and overall health.
- Staying Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support optimal bodily functions.
By adopting a holistic approach to nutrition, you can optimize your health and well-being.
There are many areas within nutrition. By keeping the above points in mind, you can take the important first steps into creating a healthy body that is not deficient in any form.
Setting Realistic Health Goals
Setting realistic health goals is an important part of your journey into fitness. A body that has high maintenance and unrealistic goals is not a body that is bound to last. Make sure to always:
- Start Small: Begin with small, achievable goals, such as reducing your intake of sugary drinks or adding more vegetables to your meals.
- Be Specific: Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a food journal or use a food tracking app to monitor your progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Celebrate Successes: Reward yourself for reaching your goals, but avoid using food as a reward.
By setting realistic health goals, you can stay motivated and make sustainable lifestyle changes.
Seeking Guidance from Health Professionals
If you’re unsure about how to interpret nutrition labels or develop a healthy eating plan, consider seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or other qualified health professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual needs and health goals.
Always take professional help into consideration when dealing with your health. As important aspects of the body, such as nutrition and diets, are complex.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🔍 Serving Size | Pay attention to the serving size on the label and adjust your intake accordingly. |
| 🍬 Added Sugars | Minimize added sugar intake to reduce risks of diabetes, heart diseases, etc. |
| 🧂 Sodium Content | Monitor sodium levels to prevent high blood pressure and heart problems. |
| 📱 Future Tech | Anticipate label innovations like FOPL and digital integrations for clearer info. |
FAQ Section
▼
The Daily Value (DV) is the recommended amount of a nutrient to consume or not exceed each day. It is listed as a percentage on the nutrition label to help you see how much of a nutrient is in one serving of the food.
▼
A food is considered low in sodium if it contains 140 mg or less of sodium per serving. Look for foods labeled as “low sodium,” “reduced sodium,” or “no salt added” to help you make healthier choices.
▼
Common sources of added sugars include soda, candy, baked goods, sweetened cereals, and processed snacks. These sugars can be disguised under names like sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, and dextrose, so read labels carefully.
▼
The nutrition information on the label is based on the serving size. Always understanding how many servings they are actually consuming and make a properly measured food.
▼
Professional advice can come from doctors, physicians, or even registered dieticians. Ask your health insurance if consultations can be reimbursed to make the check-up more worthwhile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of reading nutrition labels, especially in the context of 2025, equips you with the knowledge to make informed dietary choices. By focusing on added sugars and sodium content, understanding serving sizes, and staying informed about forthcoming label changes, you can easily navigate the complexities of food products and enhance your long-term well-being.
