Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss: The Latest Research

The latest research on the benefits of intermittent fasting for weight loss reveals promising results, indicating it can be an effective strategy for weight management and improving metabolic health.
Are you curious about the buzz around intermittent fasting (IF) and its potential for weight loss? The latest research on the benefits of intermittent fasting for weight loss offers fresh insights into how this eating pattern can impact your health and help you achieve your weight goals.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting and Its Popularity
Intermittent fasting (IF) has surged in popularity in recent years, not just as a diet trend but as a scientifically recognized approach to weight management and overall health. But what exactly is intermittent fasting, and why is it gaining so much attention?
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and voluntary fasting on a regular schedule. It’s not about what you eat, but rather when you eat.
Why is it so Popular?
The simplicity and flexibility of intermittent fasting make it appealing. Unlike restrictive diets, IF doesn’t require calorie counting or strict food choices, making it easier to adhere to in the long term.
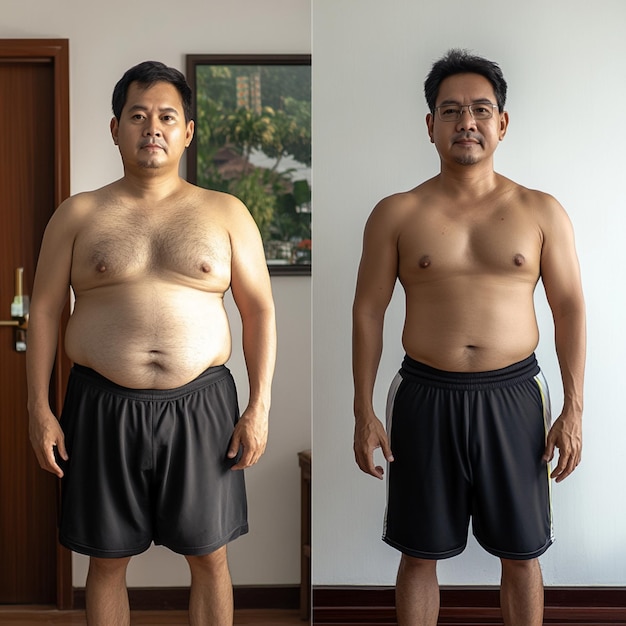

Here are some reasons individuals are drawn to this eating pattern:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Flexibility: Can be adapted to various lifestyles.
- Potential Health Benefits: Beyond weight loss, it may improve metabolic health.
In conclusion, intermittent fasting has attracted a growing number of followers due to its ease of use, adaptability, and potential health perks. As the trend continues, understanding its mechanisms and latest research becomes crucial.
The Science Behind Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss
To understand how intermittent fasting can aid in weight loss, it’s essential to delve into the biological processes that occur during fasting periods. Several key mechanisms contribute to IF’s effectiveness.
How Fasting Impacts Metabolism
During fasting, your body undergoes several metabolic shifts. As you abstain from food, insulin levels drop, which signals your body to start burning stored fat for energy.
The Role of Hormones
Hormones such as human growth hormone (HGH) and norepinephrine play a crucial role in fat metabolism. HGH, which increases during fasting, aids in fat burning and muscle preservation. Norepinephrine helps break down fat cells for energy.
Key biological processes during intermittent fasting:
- Insulin Reduction: Promotes fat burning.
- HGH Increase: Aids fat metabolism and muscle preservation.
- Cellular Repair: Activates autophagy, clearing out damaged cells.
In summary, intermittent fasting promotes weight loss by optimizing hormonal and metabolic functions. By reducing insulin levels and increasing fat-burning hormones, IF enables the body to efficiently utilize stored fat for energy.
Different Methods of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Several methods cater to different lifestyles and preferences. Understanding these variations is crucial for choosing a sustainable and effective fasting plan.
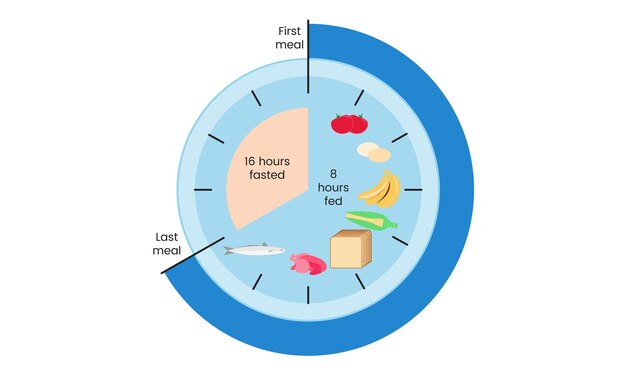
16/8 Method
The 16/8 method involves fasting for 16 hours each day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. This is one of the most popular and beginner-friendly approaches.
5:2 Diet
The 5:2 diet involves eating normally for five days of the week and restricting your calorie intake to 500-600 calories on the other two non-consecutive days.
Eat-Stop-Eat
Eat-Stop-Eat involves a 24-hour fast once or twice a week. On fasting days, you consume no calories, only water, coffee, or other non-caloric beverages.
Here’s a quick comparison of common IF methods:
- 16/8: Daily 16-hour fast.
- 5:2: Two days of restricted calories.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: 24-hour fast once or twice a week.
In conclusion, the variety of intermittent fasting methods allows individuals to find a plan that fits their lifestyle and preferences. Each method has its own benefits and challenges, so understanding the options is key to long-term success.
Recent Studies on Intermittent Fasting and Weight Loss
Recent studies have provided more evidence supporting the benefits of intermittent fasting for weight loss. Researchers are exploring different methods and their effects on various populations.
Study 1: 16/8 Method and Weight Management
A study published in the journal *Nutrition and Healthy Aging* found that the 16/8 method led to weight loss and improvements in blood pressure among obese individuals.
Study 2: 5:2 Diet and Metabolic Health
Research in the journal *Cell Metabolism* showed that the 5:2 diet improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation in overweight adults.
Key findings from recent studies include:
- Weight Loss: IF leads to significant reductions in body weight.
- Improved Metabolic Health: IF enhances insulin sensitivity.
- Reduced Inflammation: IF lowers markers of inflammation in the body.
In summary, recent studies have reaffirmed the efficacy of intermittent fasting for weight loss and metabolic health improvements. These findings provide a solid foundation for recommending IF as a strategy for weight management.
Practical Tips for Starting Intermittent Fasting
If you’re considering starting intermittent fasting, it’s important to approach it thoughtfully. Gradual implementation, proper nutrition, and listening to your body are key to a successful experience.
Start Slowly
Begin with a less restrictive method, like the 16/8, and gradually increase the fasting duration as your body adapts.
Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during fasting periods, to avoid dehydration.
Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods
When you are eating, choose whole, unprocessed foods to ensure you’re getting essential nutrients.
Here are some practical tips for success:
- Ease into it: Start with a shorter fasting period.
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water.
- Eat Well: Focus on nutrient-rich foods.
In conclusion, starting intermittent fasting requires patience and planning. By implementing these practical tips, you can ease into the routine and set yourself up for long-term success.
Potential Downsides and Who Should Avoid Intermittent Fasting
While intermittent fasting can be beneficial, it’s not for everyone. Certain groups and individuals with specific health conditions should avoid IF or consult a healthcare professional before starting.
Potential Downsides
Some people may experience side effects such as headaches, fatigue, or irritability when starting intermittent fasting.
Who Should Avoid IF
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with a history of eating disorders, and people with certain medical conditions should avoid intermittent fasting.
Situations where caution is necessary:
- Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Needs consistent nutrient intake.
- Eating Disorders: Can exacerbate unhealthy patterns.
- Medical Conditions: Consult a healthcare provider first.
In summary, intermittent fasting is not suitable for everyone. Recognizing potential downsides and contraindications is crucial to ensure safety. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine if IF is right for you.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ⏱️ Definition of IF | Cycles between eating and fasting periods. |
| 🔥 Weight Loss | Reduces insulin, burns fat for energy. |
| 🍎 Practical Tips | Start slow, hydrate, eat nutrient-dense foods. |
| ⚠️ Who Should Avoid | Pregnant, eating disorders, consult doctor for med. conditions. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Intermittent Fasting
▼
The most effective method varies by individual. 16/8 is popular for beginners, while others prefer 5:2 or Eat-Stop-Eat. Experiment to find what fits your lifestyle and goals best.
▼
Yes, black coffee or unsweetened tea is generally allowed during the fasting window. Avoid adding sugar, milk, or cream, as they contain calories that can break the fast.
▼
Results vary, but many people start seeing changes within 2-4 weeks. Consistency is key. Factors like diet, activity level, and overall health influence the speed of results.
▼
No, it’s not safe for everyone. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, people with eating disorders, and those with certain medical conditions should avoid it. Always consult your doctor.
▼
Focus on eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods and excessive sugar to maximize the benefits of IF.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the latest research on the benefits of intermittent fasting for weight loss reveals a promising approach to weight management and metabolic health. While it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, IF offers flexibility and potential benefits for those who approach it thoughtfully. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it’s right for you.
