Intermittent Fasting 2.0: Latest Guidelines & Research Findings

Intermittent Fasting 2.0 represents the updated guidelines and research findings in the field of intermittent fasting, offering insights into optimized approaches, safety measures, and potential health benefits based on recent scientific evidence.
Delve into the world of Intermittent Fasting 2.0: Updated Guidelines and the Latest Research Findings, where we unravel the evolved strategies, backed by cutting-edge research, to help you optimize your health journey with intermittent fasting.
What is Intermittent Fasting 2.0?
Intermittent Fasting (IF) has evolved, and with it, our understanding of its optimal practices. Intermittent Fasting 2.0 signifies a refined approach, incorporating the latest research findings to maximize benefits and minimize potential drawbacks.
This updated version aims to provide clearer, more evidence-based guidelines. We’ll explore what’s changed and why these changes matter for your health.
Key Updates in IF 2.0
The primary updates stem from recent studies revealing the nuances of fasting schedules and their impact on metabolic health. Understanding these nuances is key to reaping the full rewards of intermittent fasting.
- Personalized Schedules: Tailoring fasting periods to individual lifestyles and activity levels.
- Nutrient Timing: Focusing on nutrient-dense meals during eating windows for optimal health.
- Minimizing Stress: Reducing the stress response associated with rigid fasting protocols.
Research now suggests that not all IF schedules are created equal. The effectiveness depends heavily on individual factors and adherence to healthy eating patterns during non-fasting periods.
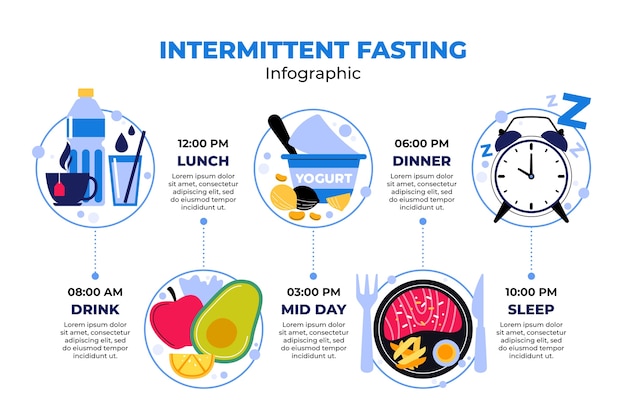
Understanding Different Intermittent Fasting Methods
Intermittent fasting isn’t a one-size-fits-all practice. Multiple methods exist, each with unique characteristics and potential benefits. Choosing the right method depends on your personal preferences and lifestyle.
From time-restricted eating to alternate-day fasting, we’ll dissect the most popular methods and their underlying principles.
Popular IF Methods
Several methods are used for intermittent fasting. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best method often depends on your individual needs and lifestyle.
- 16/8 Method: Fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window.
- 5:2 Diet: Eating normally for five days a week and restricting calorie intake on two non-consecutive days.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Fasting every other day, alternating between fasting and normal eating days.
It’s essential to understand the science behind each method and how it impacts your body. Factors such as glucose regulation, insulin sensitivity, and cellular repair play critical roles.
The Science Behind Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting’s benefits extend beyond mere weight loss. Emerging research highlights its positive impacts on metabolic health, cellular repair, and even brain function. Understanding the science can empower you to make informed choices.
We’ll delve into the key biological pathways activated by fasting, shedding light on how it promotes longevity and overall well-being.
Cellular Processes Activated
Fasting activates several important cellular processes that contribute to improved health and longevity.
- Autophagy: The body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells to regenerate newer, healthier cells.
- Mitophagy: The selective removal of dysfunctional mitochondria, promoting mitochondrial health.
- Increased Insulin Sensitivity: Improving the body’s response to insulin, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
The activation of these processes can decrease inflammation, heighten energy levels, and improve overall cellular function. It’s important to approach IF understanding these mechanisms.
Who Should Consider Intermittent Fasting 2.0?
While intermittent fasting can be beneficial for many, it’s not suitable for everyone. Certain groups should exercise caution or avoid IF altogether. Knowing if IF is right for you is crucial for a safe and effective experience.
We’ll outline the ideal candidates for IF, while also highlighting those who should proceed with caution or seek medical advice first.
Ideal Candidates for IF
Intermittent Fasting 2.0 can be a valuable tool for individuals looking to improve their metabolic health and manage their weight. However, not everyone is a suitable candidate.
Generally, healthy adults without underlying medical conditions can consider IF. Those who are overweight or obese may find IF an effective strategy for weight management.
However, there are certain groups who should approach IF with caution or avoid it altogether. These include:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with a history of eating disorders
- Those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
For these individuals, it’s vital to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any IF regimen. Personalized guidance can ensure safety and effectiveness.
Optimizing Your Intermittent Fasting Routine
Success with intermittent fasting hinges on more than just skipping meals. Optimizing your routine involves strategic nutrient timing, hydration, and stress management. A holistic approach is key to long-term adherence and health benefits.
We’ll share practical tips to help you fine-tune your IF journey, ensuring you reap the rewards without compromising your well-being.
Tips for Optimizing IF
To maximize the health benefits of intermittent fasting, consider these optimization strategies:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water, herbal teas, and non-caloric beverages during fasting periods.
- Nutrient-Dense Meals: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods during your eating windows.
- Stress Management: Implement mindfulness practices to mitigate stress-related effects.
By adopting these simple yet effective strategies, you can enhance your IF experience and achieve sustainable health improvements.
Potential Risks and How to Mitigate Them
Like any dietary approach, intermittent fasting carries potential risks. These range from mild side effects like headaches to more serious concerns like nutrient deficiencies. Understanding these risks and how to mitigate them is imperative.
We’ll equip you with the knowledge to navigate potential pitfalls, promoting a balanced and sustainable fasting experience.
Managing Potential Risks
While intermittent fasting can offer many benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks and take measures to mitigate them:
Some individuals may experience side effects such as headaches, fatigue, or irritability. These can often be managed by ensuring adequate hydration and proper nutrient intake during eating windows.
To mitigate potential nutrient deficiencies, focus on consuming a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods during your eating periods. This includes lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables.
For individuals with pre-existing health conditions, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting IF. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific needs and health status.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ⏰ Timing Matters | Adjust fasting to your daily routine for best results. |
| 🍎 Eat Well | Focus on healthy, nutrient-rich foods during eating windows. |
| 💧Stay Hydrated | Drink plenty of water and non-caloric beverages during fasts. |
| 🩺 Consult a Pro | Talk to a doctor before starting, especially with health issues. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The 16/8 method involves fasting for 16 hours each day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. It is a popular and relatively easy-to-follow approach for beginners.
▼
Yes, you can generally drink black coffee, unsweetened tea, and other non-caloric beverages during the fasting period. Avoid adding sugar or cream to maintain the fasted state.
▼
The timeline for seeing results varies, but many people report noticeable changes within a few weeks. Consistency and adherence to a healthy diet during eating windows are key factors.
▼
While IF is generally safe, it’s not suitable for everyone. Pregnant women, individuals with eating disorders, and those with certain medical conditions should consult a healthcare professional.
▼
Focus on nutrient-dense foods like lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of unhealthy fats for best results.
Conclusion
Intermittent Fasting 2.0 offers a fresh perspective on optimizing your health through strategic eating patterns. By understanding the latest research and tailoring your approach to individual needs, you can unlock the potential benefits of IF while minimizing potential risks. Always consult healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes.
